Implementing Google Analytics 4 (GA4) analytics methods is a game-changer in eCommerce, offering unprecedented insights into customer behavior and engagement. These methods are key to revolutionizing how businesses optimize their online presence and drive sales.
Let’s explore four game-changing GA4 analytics methods essential for mastering eCommerce SEO.
1. Event Tracking: Understanding Customer Interactions
Event Tracking in GA4 allows eCommerce businesses to monitor specific product-related interactions, providing deep insights into customer engagement levels. For instance, by tracking ‘Add to Cart’ events, businesses can gauge product popularity and understand product pages’ effectiveness. This data reveals customer preferences and guides inventory management and marketing strategies.
Example of Event Tracking in eCommerce
Scenario: Tracking ‘Add to Cart’ Events
Let’s say you run an online clothing store and want to understand how customers interact with your product pages, particularly focusing on the ‘Add to Cart’ action.
Setting Up the Event in GA4: First, you would set up an event in GA4 to track every time a customer clicks the ‘Add to Cart’ button on a product page. This involves tagging the ‘Add to Cart’ buttons with a unique identifier that GA4 can track.
Collecting Data: As customers browse your website and add items to their cart, GA4 records each interaction as an ‘Add to Cart’ event.
Analyzing the Data: You can then analyze this data in GA4 to see which products are being added to the cart most frequently.
This data is beneficial for multiple reasons:
Product Popularity: You can identify which products are more popular and perhaps consider stocking more of these items, offering promotions, or featuring them prominently on your site.
Customer Behavior: Understanding patterns in how different products are added to the cart can inform you about customer preferences and shopping behavior.
Effectiveness of Product Pages: Analyzing ‘Add to Cart’ events in relation to page views can give insights into the effectiveness of your product pages. A high rate of cart additions compared to views can indicate that the page is well-optimized and engaging.
Taking Action: Based on these insights, you can make informed decisions to optimize your inventory, marketing strategies, and website design to improve user experience and increase sales.
This example demonstrates how event tracking in GA4 can provide valuable insights into customer engagement with your products, allowing you to make data-driven decisions to enhance your eCommerce SEO strategy and overall business performance.
Examples of custom events:
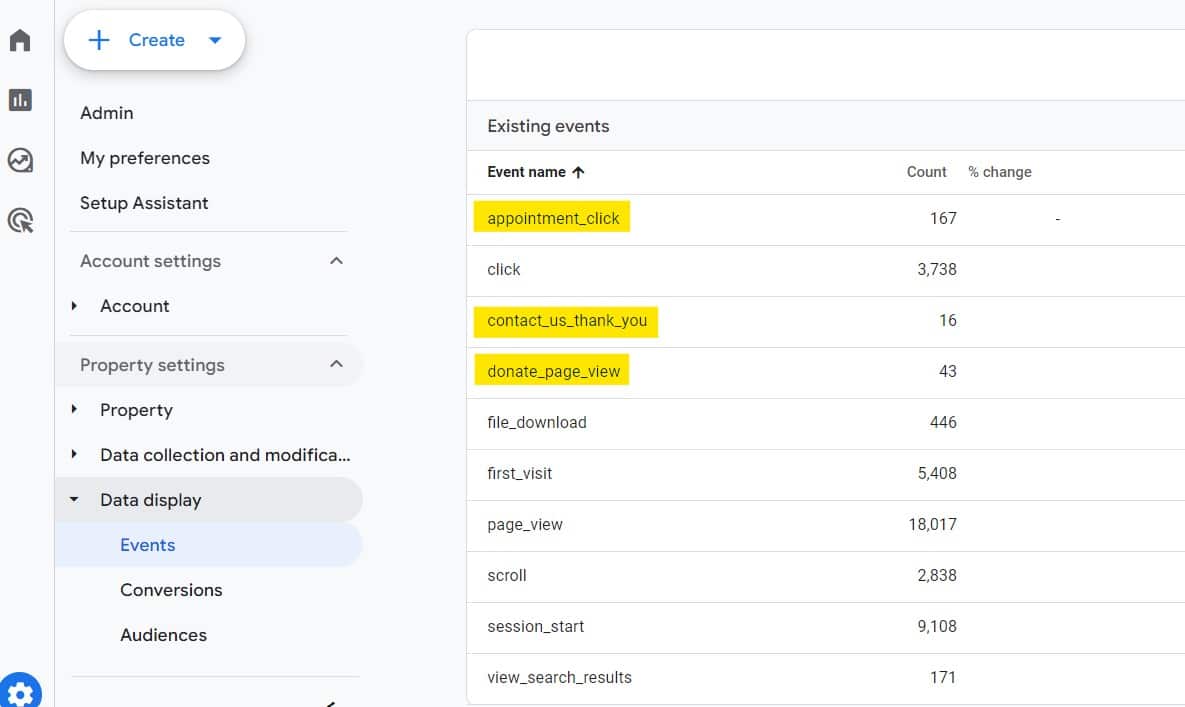
2. Segmentation and Audiences: Tailoring the Customer Experience
Segmentation and Audiences is a feature in GA4 that enables businesses to see how different customer groups interact with their products. For example, an online electronics store might segment customers based on geographic location. This segmentation can uncover regional preferences, helping businesses to customize their marketing and product offerings. Such tailored approaches lead to enhanced customer satisfaction and increased sales.
Example of Using Segmentation and Audiences in eCommerce
Scenario: Segmenting Customers Based on Geographic Location
Imagine you run an online electronics store and want to understand how customer preferences vary across different geographic locations.
Creating Segments in GA4: First, you create segments in GA4 based on geographic location. For instance, you might create segments for customers in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Collecting Data: As customers from these regions visit your website, GA4 collects data on their interactions, such as the products they view, the time spent on different product pages, and their purchasing behavior.
Analyzing the Data: You can then analyze this data to gain insights into regional preferences and behaviors.
This might reveal, for example, that:
– Customers in North America show a high interest in the latest smartphones.
– European customers are more engaged with environmentally friendly electronic products.
– Asian customers have a higher conversion rate for gaming laptops.
Tailoring Marketing and Inventory: Based on these insights, you can tailor your marketing strategies and inventory to better cater to each region’s preferences.
For instance:
– Launch targeted marketing campaigns for smartphones in North America.
– Feature eco-friendly electronics more prominently in your European store section.
– Stock more gaming laptops to meet the demand in the Asian market.
Measuring the Impact: After implementing these tailored strategies, you can continue to use GA4 to measure the impact of these changes on customer engagement and sales in each region.
This example shows how using segmentation and audience tools in GA4 can provide a deeper understanding of how different customer groups interact with your products. This valuable insight allows for more targeted and effective SEO strategies, marketing campaigns, and inventory management in your eCommerce business.
Example of active users and purchasers with state heatmap:
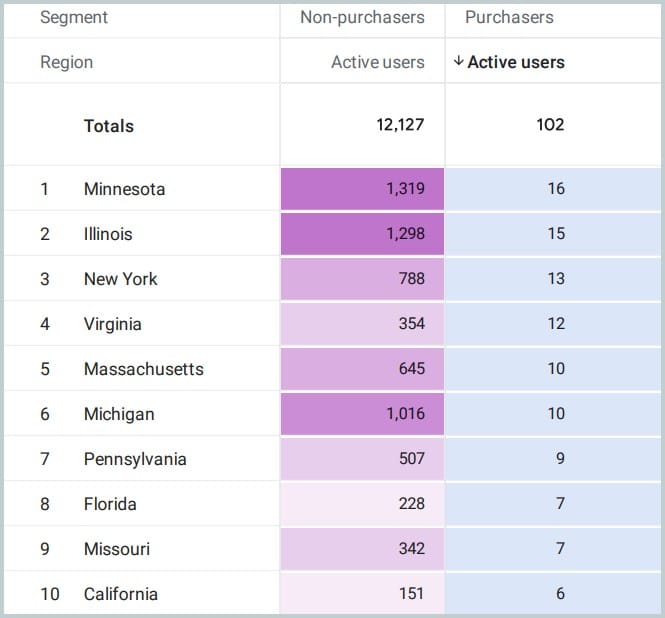
3. Funnel Analysis: Optimizing the Purchase Journey
Funnel Analysis is a critical tool in GA4 for mapping out the customer purchase journey. Businesses can identify where potential customers drop off by analyzing each step of the funnel, from viewing a product to completing a purchase. This analysis helps in pinpointing areas for improvement in the purchasing process. For instance, if there’s a significant drop-off at the checkout stage, simplifying the checkout process or adding more payment options could reduce cart abandonment rates.
Example of Funnel Analysis in eCommerce
Scenario: Analyzing the Checkout Process
Suppose you operate an online bookstore and want to analyze the customer journey from selecting a book to completing a purchase. The goal is to identify at which stages customers are dropping off and not completing their purchases.
Setting Up the Funnel in GA4: You create a funnel in GA4 that tracks the following steps:
– Step 1: Viewing a book (Product Page View)
– Step 2: Adding the book to the cart (Add to Cart)
– Step 3: Proceeding to checkout (Initiate Checkout)
– Step 4: Completing the purchase (Purchase)
Collecting and Analyzing Data: As customers interact with your website, GA4 tracks their progress through these steps. By analyzing this data, you might discover specific patterns, such as:
– A high percentage of customers view books and add them to their cart, indicating good initial engagement.
– There is a significant drop-off at the ‘Initiate Checkout’ stage, suggesting that customers are hesitating or encountering issues when they start the checkout process.
Investigating Drop-off Points: The funnel analysis highlights that the checkout process is a major drop-off point. You then investigate further to identify possible reasons, which could include:
– Complicated or lengthy checkout process.
– Lack of preferred payment options.
– Unexpected shipping costs added at checkout.
Implementing Improvements: Based on these insights, you implement changes to address these issues, such as:
– Simplifying the checkout process.
– Adding more payment options.
– Providing clearer information on shipping costs earlier in the process.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Changes: After making these changes, you continue to use funnel analysis in GA4 to measure their impact on the checkout process. Ideally, you would see a decrease in the drop-off rate at the checkout stage and increased completed purchases.
Through this example, funnel analysis in GA4 demonstrates its value in identifying critical points in the customer journey where improvements can be made. By understanding where and why potential customers are dropping off, you can take targeted actions to optimize the purchase process, thereby increasing conversion rates and overall sales for your eCommerce site.
Product funnel from product view to purchase example:
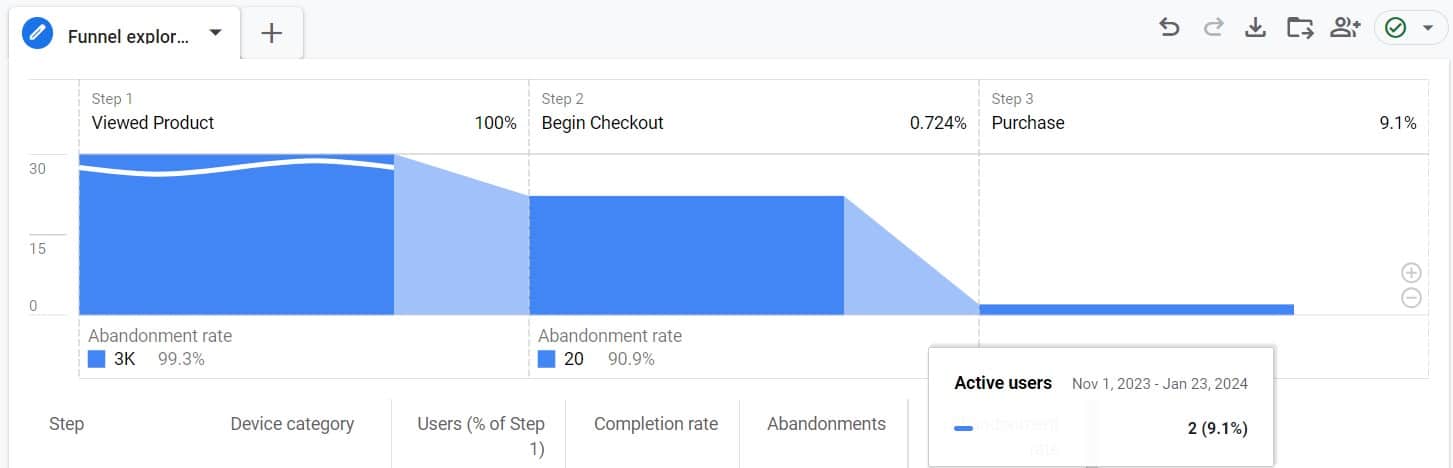
4. User Flow Analysis: Streamlining Navigation and Product Discovery
User Flow Analysis in GA4 visually represents how customers navigate through an eCommerce site. This analysis helps businesses understand the paths that lead to product interactions and purchases. For example, a home decor website can use this data to optimize the visibility of popular categories or enhance the layout of the ‘Sale’ section to encourage exploration and purchases. Understanding these navigation patterns is key to refining the user experience and boosting conversions.
Example of User Flow Analysis in eCommerce
Scenario: Tracking Customer Navigation on a Home Decor Website
Imagine you run an online store specializing in home decor. You’re interested in understanding how customers navigate your site, which products they interact with, and what paths lead to a purchase.
Setting Up User Flow in GA4: In GA4, you set up a user flow analysis to track how visitors navigate from the moment they land on your site. This flow includes multiple entry points such as the homepage, product category pages, and promotional landing pages.
Collecting and Analyzing Navigation Patterns: As users visit your site, GA4 visualizes their paths through different sections. This analysis might reveal insights like:
-Many users start at your homepage and then navigate to the ‘Living Room Decor’ category.
-A significant portion of traffic from promotional emails lands directly on product pages but doesn’t always proceed to the checkout.
-Users who visit the ‘Sale’ section often browse through multiple product pages but have a lower conversion rate.
Identifying Popular Products and Paths: You observe that certain products, like decorative cushions and table lamps, have higher interaction rates. Also, paths starting from blog posts about home decor tips often lead to product pages and result in purchases.
Optimizing the User Journey: Based on these insights, you can make strategic decisions to enhance user experience and product visibility:
-Enhance the visibility of popular categories like ‘Living Room Decor’ on the homepage.
-Optimize promotional emails to include clearer calls-to-action and direct links to the checkout page for featured products.
-Curate the ‘Sale’ section to include more high-interest products and improve the layout to encourage further exploration and purchases.
-Leverage content marketing by linking products directly in your blog posts to capitalize on the high conversion rates from these sources.
Measuring and Refining: After implementing these changes, continue to use user flow analysis to measure their impact on navigation patterns and conversion rates. This ongoing analysis helps refine strategies and further optimize your site’s customer journey.
This example shows how user flow analysis in GA4 provides a comprehensive view of how customers interact with your eCommerce site. By understanding these navigation patterns and product interactions, you can make informed decisions to streamline the user experience, enhance product discoverability, and ultimately drive more sales.
User flow from the homepage to category pages example:
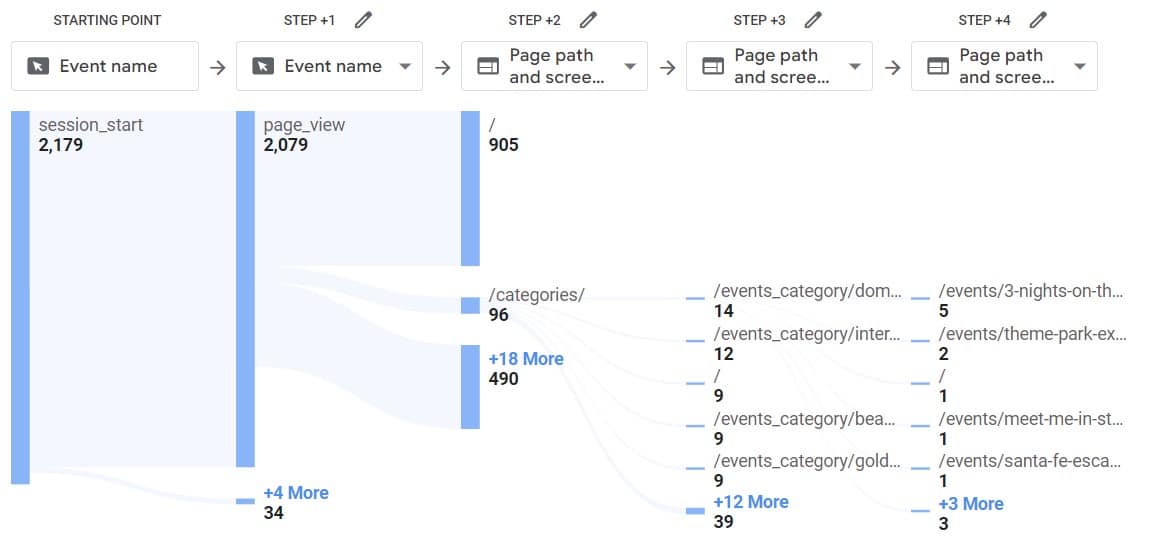
Conclusion
Leveraging these four GA4 analytics methods can revolutionize the way eCommerce businesses operate. From understanding customer behavior to optimizing the purchase process, these techniques offer a wealth of insights. In the competitive world of online retail, mastering these analytics methods is not just an advantage; it’s a necessity for sustainable growth and success.
- SEO Health Check: Ensuring Your Website’s Optimal Performance - July 16, 2024
- SEO for WordPress Websites: The Essentials - June 28, 2024
- SEO for New Websites: A Quick Start Guide - June 19, 2024
